
What Can You Make with a 3D Printer?
3D printing has come a long way since it was first developed in the 1980s. This technology is at a tipping point, about to go mainstream in a big way. Most executives and many engineers don’t realize it, but this technology has moved well beyond prototyping, rapid tooling, trinkets, and toys. Today, 3D printing is being used in an amazing number of innovative ways to help make our world a better place — on land, in the sea, and even on Mars.
Read on to discover some unexpected use cases for 3D printing that show how widely usable the technology is becoming.

3D Printed House
Today, 3D printers are capable of extruding concrete that enables the construction of various structures of varying degrees of complexity, from houses to bridges and offices.
The house you are looking at the picture above was 3D printed by a company called ICON in collaboration with New Story, a housing non-profit company in San Francisco. The two companies used 3D printing technology to produce a 350-square-foot structure that costs around $10,000 and took just 48 hours to build. Projections for 600- to-800-square foot homes based on this prototype are looking to come in under $4,000 with the approximate build time of roughly 24 hours. The two companies plan to build a whole neighborhood of these fast, affordable 3D printed houses in El Salvador. The goal is to provide homes for people who, unfortunately, don’t yet have appropriate living conditions.

3D Printed Coral Reef
The coral reefs are suffering from numerous threats such as climate change, overfishing, damage from boats, and other human-caused damage. Humans may be responsible for threatening the coral reefs, but many engineers and scientists are taking responsibility for saving and restoring them. 3D printing artificial reef structures may sound like a gimmick to draw attention, but it has been found to be an effective way of creating artificial coral reefs. 3D printing can provide temporary yet flexible enough solution to recreate complex coral shapes in a way that invites the return of sea life.
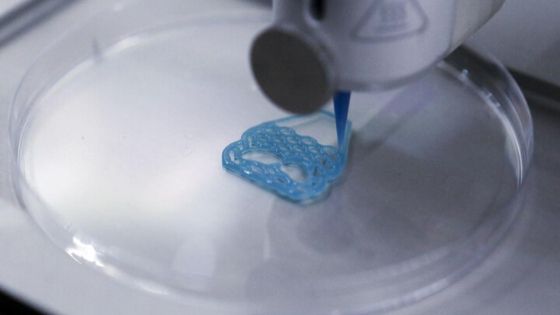
3D Bioprinting
3D Bioprinting technology is changing the future of medicine and has emerged as a powerful tool for building tissue and organ structures in the field of tissue engineering. 3D Bioprinting is an additive manufacturing process where biomaterials such as cells and growth factors are combined to create tissue-like structures that imitate natural tissues.

3D Printed Industrial Tooling
3D printing technology is one of the fastest ways to make prototypes and custom tooling, including those with complex geometry. 3D printers can significantly reduce production time which gives companies the possibility to increase their competitiveness.
Using Markforged Industrial Series 3D printers and continuous carbon fiber material, Siemens Gas & Power created a 3D printed customized circular cutting saw — and only needed to purchase the motor and blade. The Gas & Power division owns compressors, generators, and turbines around the world. Often, the gas turbine housings need maintenance, so engineers need to use a circular saw to repair them. Standard cutting saws aren’t contoured, meaning the team used to send all the components overseas, wait for the custom plate to be made, and then reassemble the tool when they received the parts back. By using 3D printed components, the team saved roughly $8,000 per tool (of which there are many) and reduced lead time by 35 days. Now, their engineers can efficiently repair turbines in the field instead of waiting on third parties.
3D printing innovation knows no bounds
These are just a few of the countless ways, from education to medicine to industry to the arts, that 3D printing technologies impact our world today. And you can be sure that the creative and diverse uses for 3D printing will continue to grow — and continue to improve the way we live and work.

